Vertical Emitting Aperture Nanoantennas
- Category: Optics & Photonics
- Tags: ami yaacobi, michael watts
Vertical input/output coupling in the telecom C-band (1535 nm << 1565 nm) has been extensively investigated for coupling to or from an optical fiber. Hence, most vertical couplers to date have size similar to fiber modal diameters (~10µm). Vertical coupling can also be used in optical phased arrays[1]),[2]) to steer a beam or generate holograms. However in a phased array, a compact structure (a few wavelengths long or less) is critical in order to fit many emitters in a small area and enable wide rotation angles with a single lobe. Most vertical couplers rely on gratings in semiconductors or insulators alone to perturb the electromagnetic field and emit efficiently. Due to the index contrasts available in dielectric structures, this method allows only weak perturbation and inherently limits the extraction rate.
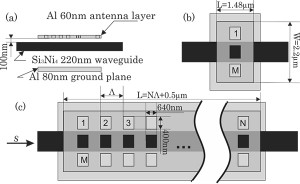
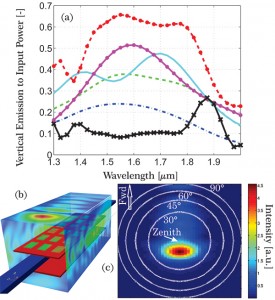
To overcome this limitation, our work[3] considers the use of metals to perturb the electromagnetic field and achieve efficient vertical coupling in a compact structure. We show that the inherent large permittivities and conductivities of metals enable large coupling coefficients and efficient output in an aperture nanoantenna, a structure only a few wavelengths long. We theoretically investigated and numerically simulated variations on the structure. In the case shown in Figure 1, we assume an aluminum nanoantenna structure is fabricated on top of a Si3N4 waveguide and an aluminum ground plane is placed below the waveguide. The ground plane breaks up/down symmetry, allowing us to couple > 50% of the light upward. Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations shown in Figure 2 reveal up to 65% coupling efficiency and a coupling bandwidth of 300nm. The use of metallic nanoantennas allows for efficient coupling in a short structure which in turn, enables the large bandwidth. The specific structure designed here is a nanophotonic aperture antenna, but the results here are general; designed properly, nanoantennas enable rapid emission from dielectric waveguides.
- Figure 1. Antenna designs: (a) side view, (b) top view of laterally repeating apertures, and (c) longitudinally repeating apertures (period Λ=0.9µm<λ/n). Bottom layer of Al represents ground plane positioned at d=3λ/4n (680nm) from emitter metal.
- Figure 2. (a) Simulated vertical emission for structures with ground-plane: (blue dash-doted) single aperture, (dashed green) 3 apertures arranged laterally to waveguide direction, (solid cyan) 3×2 array design to emit exactly to zenith, (magenta solid-w-dots) 3×2 array design for 10º backward emission, (red dashed-line-w-dots) 3×6 array design for 5º backward emission, and (black line-w-Xs) ohmic losses of 3×6 array, (b) simulated 3×6 structure with time Fourier integrated field box showing emitted fields. (c) Far field pattern of same structure at λ=1550nm.
- K. V. Acoleyen, H. Rogier and R. Baets, “Two-dimensional optical phased array antenna on silicon-on-Insulator,” Optics Express, vol. 18, pp. 13655-13660 (2010 [↩]
- J. K. Doylend, M. J. R. Heck, J. T. Bovington, J. D. Peters, L. A. Coldren, and J. E. Bowers, “Two-dimensional free-space beam steering with an optical phased array on silicon-on-insulator,” Optics Express, vol. 19, pp. 21595-21604 (2011 [↩]
- A. Yaacobi, E. Timurdogan, and M. Watts, “Vertical emitting aperture nanoantennas,” Optics Letters, vol. 37, pp. 1454-1456 (2012). [↩]