Scale-down Cell Culture for Biopharmacueticals
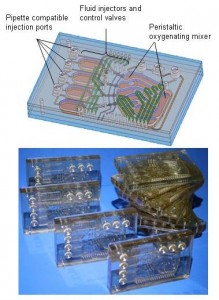
Developing highly productive cell-culture processes is an essential step in the production of biopharmaceutical products. Process development involves experimentally determining the combination of cell line, culture medium composition, and process parameters that will produce the highest quality and quantity of product. Scale-down models for large-scale bioreactors are essential for cell-culture process development in order to achieve the throughput necessary to conduct a sufficient number of experiments for a reasonable cost. Bioreactor systems based on 24 well plates [1] and a highly automated robotic system with passive microreactors [2] have recently been developed in order to overcome the shortcomings of traditional shake-flask and bench-scale stirred-tank-based scale-down models. However, in these systems mixing and fluid-handling require external machinery/robotics or manual intervention. We are using an alternative approach that integrates fluid-handling and mixing capabilities into the bioreactor device utilizing previously developed fluid injectors and mixing devices [3]. Figure 1 shows a schematic view and photographs of the mammalian-cell-culture reactor. It is fabricated with injection-molded and machined biocompatible polycarbonate layers and an actuated silicone membrane. Initial CHO cell cultures show comparable growth and viability to shake flask cultures.
- Figure 1: Schematic and photograph of integrated bioreactor device for mammalian cell culture. Device is fabricated using four layers of machined and polished polycarbonate with an elastomer membrane and adhesive bonds.
- Figure 2: Photograph of three bioreactor control modules that provide pneumatic control signals and acquire data from the optical sensors.
References
- A. Chen, R. Chitta, D. Chang, and A. Amanullah, “Twenty-Four Well Plate Miniature Bioreactor System as a Scale-Down Model for Cell Culture Process Development,” Biotechnology and Bioengineering, vol. 102, no. 1, pp. 148-160, Jan. 2009. [↩]
- A. Amanullah, J.M. Otero, M. Mikola, A. Hsu, J. Zhang, J. Aunins, H.B. Schreyer, J.A. Hope, and A.P. Russo, ” Novel Micro-Bioreactor High Throughput Technology for Cell Culture Process Development: Reproducibility and Scalability Assessment of Fed-Batch CHO Cultures,” Biotechnology and Bioengineering, vol. 106, no. 1, pp. 57-67, May 2010. [↩]
- H.L.T. Lee, P. Boccazzi, R.J. Ram, and A.J. Sinskey, “Microbioreactor arrays with integrated mixers and fluid injectors for high-throughput experimentation with pH and dissolved oxygen control,” Lab on a Chip, vol. 6, no. 9, pp. 1229-1235, Sept. 2006. [↩]