MEMS SiC Langmuir Probes for Plasma Diagnostics of Spacecraft during Reentry
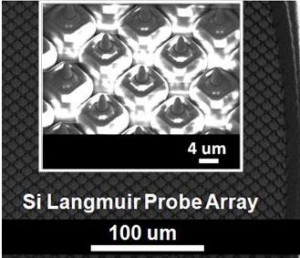
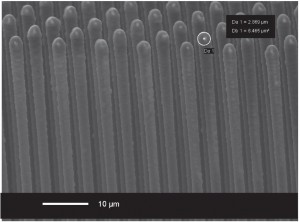
During reentry, the formation of a high-density, low-temperature plasma sheath around a spacecraft results in a communications blackout [1]. Advanced plasma sensors onboard a reentry-bound spacecraft will enhance this spacecraft’s ability to maintain communications through the plasma sheath. We propose cost-effective and reliable batch fabricated MEMS-based silicon carbide (SiC) Langmuir probe arrays to provide real-time diagnosis of plasma conditions surrounding a spacecraft during reentry. The Langmuir probe array provides data associated with specific parameters of the plasma, including plasma temperature and plasma density. The Langmuir probe array operates so that each probe in the array is individually addressable. Our MEMS-based Langmuir probe arrays are fabricated from SiC, a semiconductor material that is relatively inexpensive and very resistant to hostile environments such as spacecraft reentry [2]. Current research efforts to develop SiC-based MEMS intended for harsh environments include transistors, and transducers to measure pressure, acceleration, temperature, and strain [3] [4] [5]. Langmuir probe densities as large as 106/cm2 have been demonstrated (Figure 1). Also, fabrication experiments using plasma-enhanced chemical-vapor-deposited (PECVD) SiC coatings have been conducted (Figure 2). Future research includes the development of MEMS-based Langmuir probe arrays fabricated from SiC substrate materials and micromolded SiC. Langmuir probe performance will be validated experimentally in laboratory plasma sources that generate plasma densities similar to those encountered by spacecraft during reentry.
- Figure 1: A set of high aspect-ratio Si columns (1 μm × 1 μm × 100 μm) coated with a protective SiO2 film. The tips of the columns can be used as Langmuir probes to sample the plasma every 10 μm.
- Figure 2: A set of high-aspect-ratio Si columns coated with a PECVD SiC film.
References
- K.M. Lemmer, A.D. Gallimore, and T.B. Smith, “Using a helicon source to simulate atmospheric re-entry plasma densities and temperatures in a laboratory setting,” Plasma Sources Science and Technology, vol. 18, pp. 1-8, 2009. [↩]
- M. Wijesundara, G. Valente, W. Ashurst, R. Howe, A. Pisano, C. Carraro, and R. Maboudian, “Single-Source Chemical Vapor Deposition of 3C-SiC Films in a LPCVD Reactor I. Growth, Structure, and Chemical Characterization,” Journal of the Electrochemical Society, vol. 151, no. 3, pp. C210-C214, 2004. [↩]
- R. S. Okojie, G. M. Beheim, G. J. Saad, and E. Savrun, “Characteristics of Hermetic 6H-SiC Pressure Sensor at 600 C,” Proceedings of the AIAA Space 2001 Conference and Exposition, Albuquerque, NM, August 28-30, 2001 (AIAA Paper No. 2001-4652) [↩]
- R. S. Okojie, D. Lukco, Y. L. Chen, and D. J. Spry, “Reliability Assessment of Ti/TaSi2/Pt Ohmic Contacts on SiC After 1000 h at 600 C,” Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 91, no. 10, pp. 6553-9559, 2002. [↩]
- A. Pisano (PI), HERMIT Program at U. C. Berkeley, DARPA MTO PI Meeting, Long Beach CA, July 2007. [↩]