Architecture Design and Transmitter for Portable Ultrasound Systems
The Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasound Transducer (CMUT) is an alternative to traditional piezoelectric transducers. The CMUT technology provides an opportunity for highly integrated ultrasound-imaging system solutions because of its CMOS compatibility, ease of large array fabrication, and improved bandwidth and sensitivity performance [1].
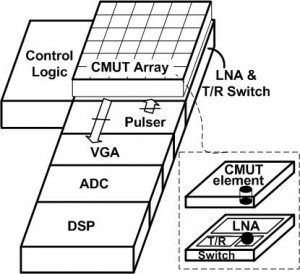
This project aims to provide a highly flexible platform for 3D ultrasound imaging. Figure 1 presents the system architecture. The CMUT device is flip-chip bonded to the supporting electronic circuits, which eliminates the cables that are usually required by traditional systems between the piezoelectric transducers and circuits. As a result, the channel count of the imaging system is increased and the capacitive loading due to cables is greatly reduced. The transmitters in the system are reconfigurable to implement Tx Beamforming; the analog front-end receivers and the DSP perform various Rx Beamforming algorithms from the received echo waveforms.
The transmitters generate high-voltage electric pulses to drive the CMUT device. The pulse magnitude should be as large as the process allows, with programmable pulse frequency at 1~10MHz and pulse duration at about 0.5~20us. In order to further increase the transmitted signal power within the transducer bandwidth, transmitter pulse-shaping is desirable. Direct waveform synthesis [2] or PWM modulation [3] are possible realizations of the transmitter pulse-shaping.
We will implement a 2D ultrasound-imaging system based on a 1D transducer and corresponding electronics as the first step. Afterwards, a 3D ultrasound-imaging system using 2D transducers will be investigated.
References
- O. Oralkan, “Acoustical Imaging Using Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer Arrays: Devices, Circuits, and systems,” Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 2004. [↩]
- P. Mercier, D. Daly, and A. Chandrakasan, “An Energy-Efficient All-Digital UWB Transmitter Employing Dual Capacitively-Coupled Pulse-Shaping Drivers,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 44, no. 6, June 2009. [↩]
- A. Dancy and A. Chandrakasan, “A Reconfigurable Dual Output Low Power Digital PWM Power Converter,” ISLPED 98, August 10-12, 1998 [↩]