A Micropower Electrocardiogram Amplifier
We have developed an electrocardiogram (EKG) preamplifier with a power consumption of 2.8μW, 8.1μVrms input-referred noise, and a Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) of 90dB. Compared to previously reported work, this amplifier represents a significant reduction in power with little compromise in signal quality [1]. The improvement in performance may be attributed to many optimizations throughout the design, including the use of subthreshold transistor operation to improve noise efficiency, gain-setting capacitors versus resistors, half-rail operation wherever possible, optimal power allocations amongst amplifier blocks, and the sizing of devices to improve matching and reduce noise. We envision that the micropower amplifier can be used as part of a wireless EKG monitoring system powered by rectified radio-frequency (RF) energy or other forms of energy harvesting.
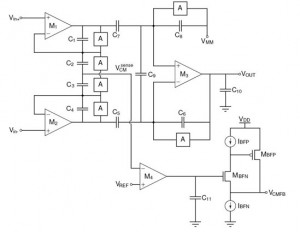
- Figure 1: Electrocardiogram amplifier schematic.
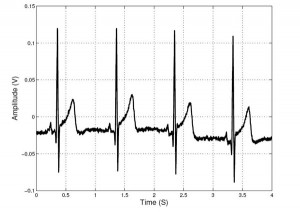
- Figure 2: Example of an EKG signal captured with the amplifier; the subject has a healthy heart.
References
- L. Fay, V. Misra, and R. Sarpeshkar, “A Micropower Electrocardiogram Amplifier,” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 312-320, Oct. 2009. [↩]