The Role of Hierarchical Morphologies in the High- performance Gas Sensing of CuO-Based Chemiresistors
- Category: Electronic Devices, Materials, Nanotechnology
- Tags: george whitfield, harry tuller
Gas sensors are essential in the monitoring, control, and reduction of harmful emissions in the environment [1] . Conductometric gas sensors based on semiconducting metal oxides are advantageous in many applications due to high sensitivity, manufacturability, and small size. However, there are a number of drawbacks, including difficulty in control over the semiconductor/substrate interface, high power consumption, and reduced selectivity at high temperatures (300-400˚C) required for operation [2] [3] . The development of gas sensors with innovative designs and advanced functional materials has attracted considerable scientific interest due to their great technological potential [4] . This work presents new insight towards the development of high-performance p-type semiconductor gas sensors. Gas sensor test devices, based on copper (II) oxide (CuO) with innovative and unique urchin-like structures, were prepared by a microwave-assisted synthesis method. An assembly of urchin-like structures was found to be most effective for hydrogen detection in the range of parts-per-billion (300 ppb) at low temperatures (200˚C). These results show that morphology plays an important role in the gas sensing performance of p-type semiconducting CuO gas sensors.
- Figure 1: SEM image of urchin-like morphology.
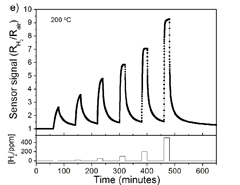
- Figure 2: Sensor response to hydrogen gas.
- F. Rock, N. Barsan, and U. Weimar, “Electronic nose: Current status and future trends,” Chemical Reviews, vol. 108, no. 2, pp. 705-725, Jan. 2008 [↩]
- K. J. Albert, N. S. Lewis, C. L. Schauer, G. A. Sotzing, S. E. Stitzel, T. P. Vaid, and D. R. Walt, “Cross-reactive chemical sensor arrays,” Chemical Reviews, vol. 100, no. 7, pp. 2595-2626, June, 2000. [↩]
- K. Wiesner, H. Knozinger, M. Fleischer, and H. Meixner, “Working mechanism of an ethanol filter for selective high-temperature methane gas sensors,” IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 354-359, Aug., 2002. [↩]
- D.-J. Yang, I. Kamienchick, D. Y. Youn, A. Rothschild, and I.-D. Kim, “Ultrasensitive and highly selective gas sensors based on electrospun SnO(2) nanofibers modified by Pd loading,” Advanced Functional Materials, vol. 20, no. 24, pp. 4258-4264, Dec., 2010. [↩]