RF MEMS Resonators in 32-nm SOI CMOS Technology
- Category: MEMS & BioMEMS
- Tags: dana weinstein, radhika marathe, wentao wang
This work presents the first hybrid RF MEMS-CMOS resonators demonstrated in silicon at the transistor level of IBM’s 32-nm SOI CMOS process, without the need for any post-processing or packaging. The unreleased, Si bulk acoustic resonators are driven capacitively and sensed using a field effect transistor (FET). MEMS-CMOS Si resonators with acoustic Bragg reflectors (ABRs) are demonstrated at 11.1 GHz with Q~18 and a footprint of 5µm × 3µm.
The majority of electromechanical devices require a release step to freely suspend moving structures, which necessitate costly complex encapsulation methods and back-end-of-line (BEOL) processing of large-scale devices [1] . Development of unreleased Si-based MEMS resonators in CMOS allows integration into front-end-of-line (FEOL) processing with no post-processing or packaging. We have previously demonstrated the Resonant Body Transistor (RBT), which employs active FET sensing of acoustic vibrations [2] [3] , which amplifies the mechanical signal before parasitics. Realization of the RBT in CMOS technology leverages high fT, high-performance transistors, enabling RF-MEMS resonators at frequencies orders of magnitude higher than possible with passive devices.
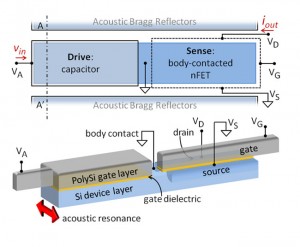
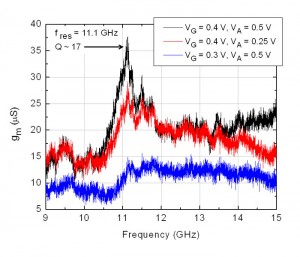
The hybrid MEMS-CMOS RBT presented in this work is a Si bulk-acoustic resonator with electrostatic drive formed using the gate dielectric and a body-contacted nFET sense transducer (see Figure 1). Acoustic vibrations in the unreleased resonator are confined using 7 pairs of 1D ABRs surrounding the device, which are patterned using shallow trench isolation (STI). The DC characteristics of the sense transistor are similar to standard body-contacted nFETs of the 32-nm SOI process and show no direct effect of the capacitor drive voltage on the FET behavior. The frequency response of an 11.1-GHz resonator is shown in Figure 2 for multiple bias conditions, verifying the mechanical nature of the resonance.
This first demonstration of an unreleased hybrid MEMS-CMOS resonator paves the way for monolithically integrated RF MEMS frequency sources and signal processors.
- Figure 1: Top and 3D views of Si-based MEMS-CMOS resonator excluding ABR. The resonator is driven capacitively on the left and sensed as a piezoresistive modulation of the nFET drain current on the right. Source and body are independently grounded.
- Figure 2: Frequency response of an 11.1-GHz nFET-ncap resonator under multiple biasing conditions of the drive voltage (VA) and gate voltage (VG).
- H. Xie, L. Erdmann, X. Zhu, K. Gabriel, and G. Fedder, “Post-CMOS processing for high-aspect-ratio integrated silicon microstructures,” Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 93-101, 2002. [↩]
- D. Weinstein and S. A. Bhave, “The resonant body transistor,” Nano Letters, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 1234-37, 2010. [↩]
- D. Weinstein and S. A. Bhave, “Acoustic resonance in an independent-gate FinFET,” in Solid State Sensor, Actuator and Microsystems Workshop(Hilton Head), 2010, pp. 459-462. [↩]