Coding Efficiency vs. Memory Cost Trade-offs for High-efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Motion Estimation
- Category: Circuits & Systems
- Tags: anantha chandrakasan, hevc, mahmut sinangil
High-efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) is a new video compression standard currently being standardized by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCTVC) established by ISO/IEO MPEG and ITU-T [1] . HEVC has a design target of 50% coding gain over AVC/H.264 High Profile. New tools are being adopted to HEVC in order to achieve this goal. However, it is also important to consider the hardware cost (in terms of memory area and data bandwidth) of these tools. Larger memory area and bandwidth generally result in higher power consumption, which can be a limiting factor in various applications such as portable multimedia and mobile devices. Hence, having a memory size and bandwidth vs. coding efficiency trade-off for different tools and different blocks is important for making high-level design decisions.
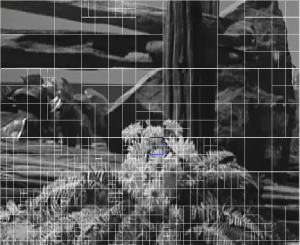
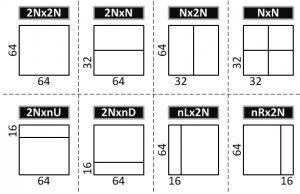
One of the main differences of HEVC from previous video compression standards is the coding tree structure. In this structure, a frame is first divided into largest coding units (LCUs). Then an LCU is further divided into coding units (CUs) in a quad-tree structure. Unless a CU is further divided into four smaller CUs, it is predicted with one of several PU (prediction unit) types as shown in Figure 1 [2] . Currently, LCU size can be as large as 64×64 and smallest CU (SCU) can be as small as 8×8. For inter-prediction, there are many different PU types as shown in Figure 2. 2Nx2N, 2NxN, Nx2N and NxN are main PU types where 2Nx2N corresponds to the size of the CU. If asymmetric motion partitions (AMP) are used, non-square PUs for inter-prediction also include 2NxnU, 2NxnD, nLx2N and nRx2N. NxN is allowed only at the SCU level. On the encoder side, decisions can be made to support only a subset of these PU types and CU sizes. This limitation will present a trade-off between hardware complexity and coding efficiency.
- Figure 1: An example of a frame partition with the coding quad-tree structure [2]. Highly detailed areas are coded using smaller block sizes.
- Figure 2: PU types in inter-prediction in a 64×64 LCU. Square-shaped as well as rectangular-shaped prediction units are used to improve coding efficiency.
- “Joint call for proposals on video compression technology,” ITU-T SG16/Q6, 39th VCEG Meeting, Kyoto, 17-22 Jan. 2010, Doc. VCEGAM91. [↩]
- T. Lu, X. Lu, Q. Xu, Y. Zheng, J. Sole, and P. Ying, “A video coding analyzer for next-generation compression standards,” IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics, pp. 707-708, Jan. 2011. [↩]