An Ultra-low-power ISM-band Transmitter with Tunable Channel-Network Coding
- Category: Circuits & Systems, Medical Electronics
- Tags: anantha chandrakasan, georgios angelopoulos
Designing a low-power wireless communication system involves two major milestones: use of very efficient RF architectures, including circuits for power amplifiers, mixers, etc., as well as employing the appropriate protocol-level algorithms, such as forward error correction (FEC) codes, CRCs, etc. Although these two steps are usually performed in isolation, the result has been extremely successful for designing efficient long-distance communication systems. However, this approach is highly suboptimal for short-range communication systems (i.e., Body Area Networks), where the power consumption of these two components can be comparable [1] . For this reason, very careful, system-level analysis is required to achieve the minimum energy consumption in transmitting the required information.
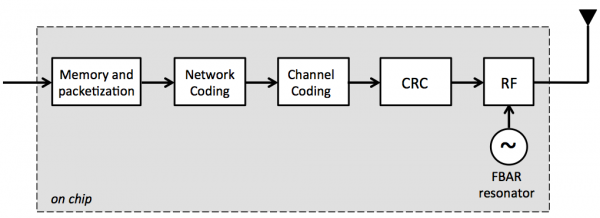
We have designed a flexible, ultra-low-power ISM-band transmitter, including baseband processing and basic protocol functionality (i.e., packetization, CRC calculation), using a 65-nm TSMC process. The simplistic block diagram of the transmitter is shown in Figure 1. The fabricated chip includes four memory banks to store incoming data, a tunable convolutional encoder optimized for short-distance RF modules, and an RF transmitter that utilizes a high-Q FBAR resonator as a local oscillator [2] . The transmitter has an output power of ~-10dBm and supports 1Mbps OOK and FSK modulation. An on-chip FIR filter implements Gaussian pulse shaping for GFSK modulation. In addition to the FEC code, the transmitter has a dedicated accelerator implementing a new form of coding, called network coding (NC) [3] , which can increase the reliability of the communication system under challenged channel conditions and potentially reduce the required amount of energy communicating information.
- P. Grover, K. Woyach, and A. Sahai, “Towards a communication-theoretic understanding of system-level power consumption,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 29, no. 8, pp. 1744-1755, Sept. 2011. [↩]
- A. Paidimarri, “Architecture for ultra-low powermulti-channel transmitters for body area networks using RF Resonators,” Master’s thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, 2011. [↩]
- R. Koetter and M. Medard, “An algebraic approach to network coding,” IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 782- 795, Oct. 2003. [↩]