A Low-power, Reconfigurable Body Area Network for Healthcare Monitoring
- Category: Circuits & Systems, Medical Electronics
- Tags: anantha chandrakasan, healthcare, nachiket desai
Advancements in low-power electronics have opened up many opportunities to provide healthcare solutions through continuous, unobtrusive sensing of vital physiological signs. Power budgets and, by extension, size and cost of such sensors are now dominated by the communication costs, which have not scaled as rapidly [1] . We are working on a topology and associated protocols customized for such networks that relax power requirements enough for the network itself to power sensors.
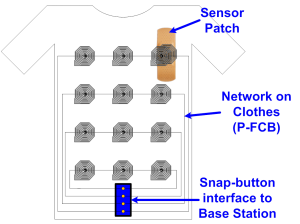
The network consists of clothing made from e-textiles containing a number of strategically-placed inductors screen-printed using a silver paste [2] . Sensor Nodes (SNs) can be placed beneath any number of inductors. Power is transferred from the central Base Station (BS) to the SNs in the 27-MHz ISM band, which eliminates the need for bulky energy sources at each SN. Data from the SN is transferred at 1 Mbps through an impedance modulation link, similar to RFID, and is perceived as an ASK waveform by the BS. The high data rate allows each SN to have a very low transmit duty cycle (~1-2 %).
The medium-access protocol is designed to minimize the decision-making burden on the SN. Upon configuring the network, each SN is classified as a “Stream” mode (e.g., EKG, EEG) sensor or a “Contention Access (CA)” mode (e.g., blood pressure, glucose) sensor, which sends data infrequently. The BS assigns fixed timeslots to each stream-mode sensor. Once it has looped through all such sensors, it opens a CA period for the other sensors in the network. The protocol ensures that an SN always waits for a signal from the BS before transmitting and renders synchronization routines, such as the one presented in [3] , unnecessary.
- Figure 1: Architecture of e-textile network. Inductors on the fabric are arranged according to physical or functional proximity. A snap-button interface is used for connecting to the BS to avoid two inductive hops.
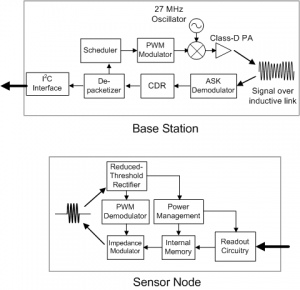
- Figure 2: Block diagrams of Base Station and Sensor Node. Network access and configuration instructions are transmitted by the BS using an RZ PWM scheme to enable non-coherent detection at SN [4].Figure 2: Block diagrams of Base Station and Sensor Node. Network access and configuration instructions are transmitted by the BS using an RZ PWM scheme to enable non-coherent detection at SN [4] .
- N. Verma, A, Shoeb, J. Bohorquez, J. Dawson, J. Guttag, and A. P. Chandrakasan, “A micro-power EEG acquisition SoC with integrated feature extraction processor for a chronic seizure detection system,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 804-816, Apr. 2010. [↩]
- K. Yongsang, K. Hyejung, and Y. Hoi-Jun, “Electrical characterization of screen-printed circuits on the fabric,” IEEE Transactions on Advanced Packaging, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 196-205, Feb. 2010. [↩]
- O. Omeni, A. Wong, A. J. Burdett, and C. Toumazou, “Energy efficient medium access protocol for wireless medical Body Area SSensor Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, vol.2, no. 4, pp. 251-259, Dec. 2008. [↩]
- S. Mandal and R. Sarpeshkar, “Power-efficient impedance-modulation wireless data links for biomedical implants,” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, vol. 2, p. 301, 2008. [↩]