Virtual-source-based Self-consistent Charge and Transport Models for Ballistic MOSFETs
- Category: Electronic Devices
- Tags: Dimitri Antoniadis, Lan Wei, Omar Mysore
Compact models describing the voltage-dependent terminal current and charges (or equivalently, capacitances) are essential for small-signal and transient circuit simulation. In this work, we extend the virtual-source (VS)-based transport model [1] with a self-consistent channel charge model for quasi-ballistic or fully ballistic devices, when the gradual channel approximation (GCA) and the drift transport theory are no longer valid. From a parabolic channel potential profile approximation and current continuity boundary condition, we derive a voltage-dependent charge model that is self-consistent with the transport model in the ballistic regime. The extended VS model has been implemented in Verilog-A language. [2]
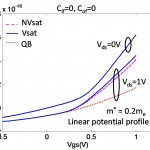
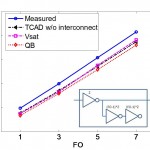
Devices operating in the ballistic regime in saturation have less channel charge than predicted by the drift-diffusion theories, which is in principle advantageous from the performance point of view. The quasi-ballistic (QB) model predicts 61% and 58% fewer intrinsic channel charges than the saturation velocity model (Vsat) and non-saturation drift velocity model (NVsat), respectively (Figure 1). The difference diminishes in the linear region or because the device essentially operates with low carrier velocity and a lot of scattering with low Vgs or Vds. It is also shown that the benefits of fast carrier transport in tight-pitch logic circuits diminish due to the presence of extrinsic charges, particularly at higher fan-outs. As shown in Figure 2, the stage delay of a 5-stage ring oscillator predicted by QB model is only 5% and 3% less than that by Vsat and Nsat models, respectively. However, for RF applications the benefit of quasi-ballisticity in Si or near-full ballisticity in III-V HEMTs calculated by the model can be significant.
- Figure 1: Channel charges associated with the gate terminal under different charge models without extrinsic capacitances. QB model predicts a 61% and 58% less intrinsic channel charge than Vsat and NVsat models at Vds=Vgs=1V, respectively.
- Figure 2: Stage delay of a 5-stage ring oscillator with different charge models. QB model predicts only a 5% and 3% less delay than Vsat and NVsat models, respectively.
- A. Khakifirooz, O. Nayfeh, and D. Antoniadis, “A simple semiempirical short-channel MOSFET current-voltage model continuous across all regions of operation and employing only physical parameters,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices,, vol. 56, pp. 1674-1680, 2009. [↩]
- L. Wei, O. Mysore, and D. Antoniadis, “Virtual-source based self-consistent charge and transport models for near-ballistic FETs,” to be submitted to 2011 International Electron Devices Meeting. [↩]