Thermal Ink Jet Printing of PZT Thin Films
- Category: MEMS & BioMEMS
- Tags: Sang-Gook Kim, Stephen Bathurst
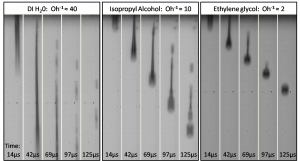
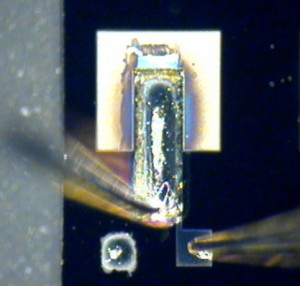
We recently demonstrated a process of thermal ink jet printing of PZT thin films for MEMS applications [1] [2] . Previous methods for deposition of solution-based PZT were painstaking and low-yield; they also imposed significant processing and design constraints. Thermal ink jet printing allows for rapid, low-cost deposition of patterned PZT films over a wide range of geometries and provides for greater flexibility in process sequencing. With this technique, PZT may be easily integrated into devices with large out-of-plane features after the micro-machining process, which enables the formation of more complex device structures. In 2010-2011 the printing process was modeled in detail, including the dynamics of droplet formation as well as the internal flows that occurring during film drying. Models proposed by others were extended to include printed PZT films [3] . Experiments were carried out to confirm the modeling. Specifically, high-speed camera images (Figure 1) were taken to visualize the droplet formation, and the effects of surface tension and temperature were investigated through droplet drying tests. As a result the conditions required for highly repeatable and uniform printed films were determined. Further development work focused on the integration of printed PZT into a range of micro-machined structures including cantilevers and bridges with energy harvester applications as well as resonators for ultrasonic transduction (Figure 2). These devices provide a proof of concept for a fully integrated PZT device fabrication process. In the future we plan to produce devices that utilize the full capabilities of this process to reach energy densities and acoustic coupling greater than those of devices based on current deposition techniques.
- Figure 1: High-speed images of droplets ejected from a thermal ink jet nozzle. Images confirm that the range of stable droplet formation occurs when the inverse Ohnesorge number (the ratio of viscous to surface tension forces) is between 1-3.
- Figure 2: Testing of a printed PZT cantilever. PZT deposition was carried out after the micromachining process.
- S. P. Bathurst and S. G. Kim, “Designing direct printing process for improved piezoelectric micro-devices,” CIRP Annals – Manufacturing Technology, vol. 58, pp. 193-196, 2009. [↩]
- S. P. Bathurst, H. W. Lee, and S. G. Kim, “Ink jet printing of PZT thin films for MEMS applications,” Proc. International Conference on Digital Fabrication, 2008, pp. 897-901. [↩]
- H. Hu and R. G. Larson, “Marangoni effect reverses coffee-ring depositions,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 110, , pp. 7090-7094, Apr. 2006. [↩]