Spin Injection in Organic Semiconductors for its Use in OLEDs: The Bathophenantroline Case
- Category: Electronic Devices
- Tags: David Ciudad, Marc Baldo
Recently, the demonstration of spin injection and transport in hybrid organic semiconductor (OS)-based devices [1] [2] [3] and the use of OS as spin tunnel barriers [4] [5] [6] [7] have induced a great interest in using organic materials in spintronics, (“spin-based electronics”). This is a new electronics paradigm whose goal is to use the spin of the electrons to produce faster, low-consumption, and cheaper electronic and optoelectronic devices. The spin dynamics underlying the spin transport in OS is subject to interesting scientific debate. The role of the nature and properties of the materials used, and the interfaces between OS and magnetic materials, need to be clarified [8] .
Our research studies the effect of magnetic fields on the performance of OLEDs and solar cells. The efficiency of OLEDs could in principle be doubled by injecting a spin polarized current [9] . The role of the materials’ properties used and the interfaces between OS and magnetic materials need to be investigated.
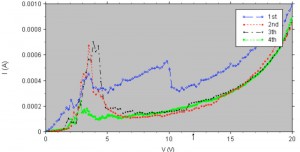
A key problem for spin injection is the energy mismatch between the metal and the semiconductor. It forces to use relatively high voltage bias in order to get appreciable currents in the devices. These voltages destroy the spin information. To avoid this problem we used bathophenantroline (BPhen) since doping with lithium greatly reduced the energy mismatch. Some functional OLEDs have been produced, but they are found to be unstable, as Figure 1 shows.
Another issue in the organic semiconductor is the spin diffusion length (λS), which is the distance over which the spin polarization is reduced 1/e times its initial value. Even if the injection of the spin polarized current is achieved, λS will limit the spin polarization.
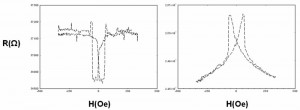
To study this parameter in BPhen, we have developed BPhen-based spin valves. λS can be determined by measuring the magneto-resistance (MR) through different channel lengths. MR is the relative change of the resistance depending on the parallel or anti-parallel magnetization of the electrodes. The spin diffusion length is derived by fitting the MR experimental data versus the channel length (organic semiconductor thickness in our vertical spin valve) with the modified Jullière formula [2] . The BPhen-based spin valves seem to be unstable. Surprisingly, both positive and negative tunnel magneto-resistance (TMR) values have been found in the same set of samples. See Figure 2. The instability of the BPhen-based OLEDs and spin valves may be related to the low glass transition of BPhen [10] .
We are exploring the spin injection processes in organic semiconductors that include magnetic atoms. Our studies show ferrocene to be dissociated when its thermal deposition is attempted. We are studying the promising materials cobalt, nickel, and iron phthalocyanines.
- Figure 1: BPhen-based OLEDs. We have used cobalt electrodes and alumina barriers for spin injection. The picture shows 4 consecutive measurements in the same device. It is unstable.
- Figure 2: Magneto-resistance (MR) measurements in BPhen spin valves: Co/BPhen/FeNi
- V. Dediu, M. Mirgoa. F. C. Matacotta, C. Taliani, and S. Barbanera. Sol. State. Commun. vol. 122, p. 181, 2002. [↩]
- Z. H. Xiong, D. Wu, Z. V. Vardeny, and J. Shi, Nature vol. 427, p. 821, 2004. [↩] [↩]
- L. E. Hueso, A. Riminucci, I. Bergenti, Y. Zhan, and V. Dediu, Adv. Mater. vol. 19, p. 2639, 2007. [↩]
- J. R. Petta, S. K. Slater, and D. C. Ralph, Phys. Rev. Lett. vol. 93, p. 136601, 2004. [↩]
- T. X. Wang, H. X. Wei, Z. M. Zeng, X. F. Han, Z. M. Hong, and G.Q. Shi, Appl. Phys. Lett. vol. 88, p. 242505, 2006. [↩]
- W. Wang and C. A. Richter, Appl. Phys. Lett. vol. 89, p. 153105, 2006. [↩]
- T. S. Santos, J. S. Lee, P. Migdal, I. C. Lekshmi, B. Satpati, and J. S. Moodera, Phys. Rev. Lett. vol. 98, p. 016601, 2007. [↩]
- C. Barraud, P. Seneor, R. Mattana, S. Fusil, K. Bouzehouane, C. Deranlot, P. Graziosi, L. Hueso, I. Bergenti, V. Dediu, F. Petroff, and A. Fert, Nature Physics, vol. 6, p. 615, 2010. [↩]
- I. Bergenti, V. Dediu, E. Arisi, T. Mertelj, M. Murgia, A. Riminucci, G. Ruani, M. Solzi, and C. Taliani, Organic Electronics, vol. 5, pp. 309-314, 2004. [↩]
- L. Chen, G. Dong, L. Duan, L.Wang, J. Qiao, D. Zhang, and Y. Qiu, J. Phys. Chem. C, vol.113, p. 16549, 2009 [↩]