A Wearable Vital Signs Monitor at the Ear
- Category: Circuits & Systems, Medical Electronics
- Tags: Charles Sodini, CICS, David He, Eric Winokur
Vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygenation, cardiac output, and respiratory rate are necessary in determining the overall health of a patient. Continuous monitoring of these vital signs can help assess the wearer’s overall state of health and identify risks for cardiovascular diseases [1] .
We propose the site behind the ear as a location for an integrated wearable vital signs monitor [2] . This location offers physiological signals such as the electrocardiogram (ECG), the photoplethysmogram (PPG), and the head ballistocardiogram (hBCG). The ECG measures the electrical activity from the heart and offers information such as continuous heart rate, blood pressure (when coupled with PPG or hBCG), and respiratory rate. The PPG measures the blood volume and color under the skin using optical illumination. The PPG offers information such as continuous heart rate and blood oxygenation. The hBCG measures the head’s mechanical reaction to the blood expelled by the heart and offers information about continuous heart rate, cardiac output, and respiratory rate.
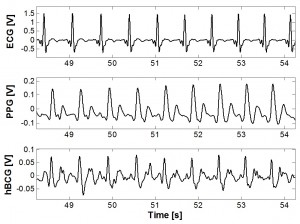
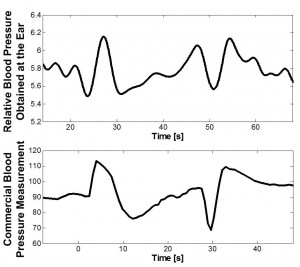
A simultaneous measurement of ECG, PPG, and hBCG is shown in Figure 1. Using the peak timing data from ECG, PPG, and hBCG, blood pressure can be estimated. Figure 2 compares the estimated blood pressure with a commercial blood pressure measurement during a Valsalva breath-hold maneuver.
To make the monitor wearable, the electrodes must be small, comfortable, and gel-less to avoid skin irritation. We use 1-cm2 capacitive and dry electrodes made of wearable fabric materials. The device is designed to use the ear as a discreet and a natural anchor that reduces device visibility and the need for skin adhesives.
- Figure 1: Simultaneous measurements of chest ECG, ear PPG, and ear hBCG.
- Figure 2: Top – Estimated relative blood pressure using ECG and hBCG timing data during a Valsalva maneuver. Bottom – Commercial blood pressure measurement during a Valsalva maneuver.
- S. D. Pierdomenico, M. Di Nicola, A. L. Esposito, R. Di Mascio, E. Ballone, D. Lapenna, F. Cuccurullo, “Prognostic value of different indices of blood pressure variability in hypertensive patients,” American Journal of Hypertension, vol. 22(8), pp. 842-847, June 2009. [↩]
- D. He, E. S. Winokur, T. Heldt, C. G. Sodini, “The ear as a location for wearable vital signs monitoring,” Proc. of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Conference, Sept. 2010, pp. 6389-6392. [↩]